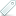
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (Beyond The Basics): Patient Information – The Thin Inner Layer Is Called The Endometrium
 The inside of the uterus has two layers.
The inside of the uterus has two layers.
In women who ovulate and menstruate regularly, the endometrium thickens nearly any month in preparation for pregnancy. These and similar causes are discussed in the next section. However, abnormal bleeding in teens can also be caused by most of the conditions that cause bleeding in all premenopausal women. Ok, and now one of the most important parts. Menstruation occurs 10 to 14 days after ovulation. So endometrial lining is shed throughout the menstrual period, Therefore in case the woman does not become pregnant. Notice, the thick outer muscular wall is the myometrium. Lining normally stops growing and shedding, after menopause. Anyway, the thin inner layer is called the endometrium.
Under normal circumstances, a woman’s uterus sheds a limited percentage of blood during any menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs erratically or excessive regular menstrual bleeding is considered to be abnormal uterine bleeding. Furthermore, any uterine bleeding is considered abnormal, if a woman who isn’t taking hormone therapy enters menopause and the menstrual cycles have ended. Throughout the pelvic exam, the clinician will look for any obvious lesions and will examine the size and shape of the uterus. Clinician will perform a physical examination to evaluate the woman’s overall health, and a pelvic examination to confirm that the bleeding is from the uterus and not from another site.
During the biopsy, a thin instrument is inserted through the vagina into the uterus to obtain a small sample of endometrial tissue.
It can occur at any time in the course of the reproductive years, anovulation is most common when periods first begin and during perimenopause. Some women do not ovulate regularly and may experience unpredictable light or heavy vaginal bleeding. Biopsy may miss and identical tests are sometimes necessary, as long as only a small portion of the endometrium is sampled. I am sure that the biopsy can be performed in a healthcare provider’s office without anesthesia.
Some women who ovulate regularly experience excessive blood loss during their periods or bleed between periods.
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding. Fibroids, adenomyosis and polyps can also occur in anovulatory women. For instance, while adenomyosis is a condition in which the lining of the uterus grows into the myometrium, fibroids are benign masses in the muscle layer of the uterus. Of course, patient information. Endometrial polyps are fleshy growths of tissue which project into the uterine cavity. On top of that, the most common causes of such bleeding are uterine fibroids, uterine adenomyosis, or endometrial polyps. These conditions are common causes of abnormal uterine bleeding.
Other causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in premenopausal women include. In this situation, mostly there’s a risk that the woman could become pregnant if she has sex. Then again, breakthrough bleeding can also happen if a hormonal birth control method is forgotten or taken late.
Women in the menopausal transition are also at risk for other conditions that cause abnormal bleeding, including cancer, infection, and bodywide illnesses.
This topic review discusses the possible causes of abnormal bleeding, how it’s evaluated, and various treatments that can be recommended. Further evaluation is needed in women with persistent irregular menstrual cycles or an episode of profuse bleeding. Abnormal uterine bleeding can be caused by many different conditions.
ABNORMAL UTERINE BLEEDING TREATMENT
The treatment of abnormal bleeding is based upon the underlying cause. Therefore this article may be updated as needed on our web site.
Progestins may also be given in other ways, just like in an injection, an implant, or an intrauterine device.
Some women completely stop having menstrual bleeding for a reason of the IUD, that is reversible when the IUD is removed. These treatments are discussed in detail in a separate topic review. Progestinreleasing IUDs decrease menstrual blood loss by more than 50 percent and decrease pain associated with periods.
women with fibroids can have surgical treatment of their fibroids, either by removing the fibroid or by reducing the blood supply of the fibroids. Most definitive surgical treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding is hysterectomy, or removal of the entire uterus. Hysterectomy might be performed by conventional laparoscopy or robotic laparoscopy, through the vagina, or by an open incision on the abdomen. WHERE TO GET MORE INFORMATION
Your healthcare provider is top-notch source of information for questions and concerns about your medical problem. At the time of hysterectomy, the ovaries might be left in place or removed. More information about these treatments is available separately.
Recent Posts
- When to Call for Vaginal Bleeding
- Treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding
- Women’s Health St Petersburg
Categories
- a healthy woman
- abnormal bleeding
- abnormal bleeding after period
- abnormal bleeding between periods
- abnormal bleeding between periods causes
- abnormal bleeding during period
- abnormal bleeding in between periods
- abnormal menstrual bleeding
- abnormal period
- abnormal period cycle
- abnormal period pain
- abnormal period spotting
- abnormal spotting
- abnormal spotting after period
- abnormal spotting between periods
- abnormally heavy period
- abnormally long period
- after period bleeding
- after period spotting
- after period still bleeding
- after period still spotting
- all women health center
- all women's health
- articles on women's issues
- between period bleeding
- black period blood
- bleed between periods
- bleeding after a period
- bleeding after few days of periods
- bleeding after having period
- bleeding after menses
- bleeding after menses over
- bleeding after menstrual cycle
- bleeding after menstrual period
- bleeding after menstruation
- bleeding after menstruation days
- bleeding after my period
- Bleeding After Period
- bleeding after period causes
- bleeding after period ends
- bleeding after period finished
- bleeding after periods over
- bleeding after your period
- bleeding and discharge between periods
- bleeding and not on your period
- bleeding and not period
- bleeding and spotting between periods
- bleeding before periods causes
- bleeding between cycles
- bleeding between menses
- bleeding between menstrual cycles
- bleeding between menstrual periods
- bleeding between periods
- bleeding between periods after pregnancy
- bleeding between periods causes
- bleeding days after period
- bleeding during cycle
- bleeding even after period
- bleeding few days after period
- bleeding for a month
- bleeding for a week after period
- bleeding heavily between periods
- bleeding heavily in between periods
- bleeding heavy after period
- bleeding in between cycles
- bleeding in between menstrual cycle
- bleeding in between periods
- bleeding in between periods causes
- bleeding inbetween periods
- bleeding not during period
- bleeding not on your period
- bleeding not period
- bleeding off and on after period
- bleeding on and off after period
- bleeding period
- bleeding spotting
- bleeding spotting between periods
- bleeding week after period
- blood after menstrual cycle
- blood after menstruation
- blood after period
- blood between periods
- blood clots during period
- blood clots in period
- blood spots after period
- blood spotting
- blood spotting after period
- blood spotting between periods
- blood spotting causes
- blood spotting in between periods
- breakthrough bleeding
- breakthrough bleeding between periods
- brown period
- brown period blood
- calculate my period
- can you bleed a week after your period
- can you have spotting after your period
- cause of bleeding after menstrual cycle
- causes bleeding between periods
- causes bleeding in between periods
- causes for bleeding after period
- causes for bleeding between periods
- causes for bleeding in between periods
- causes for heavy menstrual bleeding
- causes for spotting after period
- causes for spotting between periods
- causes heavy bleeding between periods
- causes light bleeding between periods
- causes of abnormal menstrual cycle
- causes of bleeding after menstruation
- causes of bleeding after period
- causes of bleeding after period finished
- causes of bleeding before menstrual period
- causes of bleeding between periods
- causes of bleeding in between periods
- causes of bleeding in women
- causes of bleeding inbetween periods
- causes of excessive menstrual bleeding
- causes of heavy bleeding between periods
- causes of heavy periods
- causes of irregular bleeding
- causes of irregular periods
- causes of irregular periods and spotting
- causes of light bleeding after period
- causes of light bleeding between periods
- causes of light spotting between periods
- causes of period spotting
- causes of prolonged menstrual bleeding
- causes of spotting after menstruation
- causes of spotting after period
- causes of spotting between periods
- causes of spotting in between periods
- causes of spotting in women
- causes of spotting period
- causes of uterine bleeding between periods
- centers for women's health
- cervical pain during period
- clots during period
- common causes of spotting
- common female health problems
- common health problems in women
- constant bleeding after period
- constant bleeding between periods
- constant menstrual bleeding
- constant spotting after period
- constant spotting between periods
- continued bleeding after period
- continued spotting after period
- continuing bleeding after period
- continuous bleeding after menstruation
- continuous bleeding after period
- continuous bleeding between periods
- continuous light bleeding after period
- continuous menstrual bleeding
- continuous spotting after period
- continuous spotting between periods
- cramps before period
- cramps but no period
- cure for heavy periods
- cures for heavy menstrual bleeding
- dark period blood
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- early heavy period
- early period
- erratic bleeding between periods
- excess bleeding after period
- excessive bleeding between periods
- excessive bleeding during menstruation
- excessive bleeding during period
- excessive bleeding period
- excessive period bleeding
- extended bleeding after period
- extended menstrual bleeding
- extra bleeding after period
- extra bleeding between periods
- extra heavy period
- extremely heavy period
- female bleeding not period
- female fitness websites
- female health
- female health and fitness
- female health clinic
- female health issues
- female health problems
- female health questions
- female health tips
- female healthcare
- female issues in health
- female medical issues
- female medical questions
- female period
- female spotting after period
- female spotting causes
- fit and healthy women
- fitness sites for women
- fitness websites for women
- free womans health clinic
- frequent bleeding between periods
- frequent menstrual periods
- frequent spotting between periods
- girls having periods
- girls period
- having spotting after period
- health
- health 4 women
- health advice for women
- health and fitness for women
- health and fitness websites
- health and fitness women
- health and wellness for women
- health and women
- health articles
- health articles for women
- health care women
- health female
- health for women
- health in women
- health issues
- health issues affecting women
- health issues for women
- health issues in women
- health issues of women
- health magazine
- health magazine australia
- health magazines for women
- health news
- health of women
- health problems in women
- health problems of women
- health resources
- health services for women
- health sites
- health tips
- health tips for women
- health tips women
- health topics for women
- health websites
- health websites for women
- healthcare
- healthcare for women
- healthy female
- healthy ladies
- healthy lady
- healthy women
- heavy abnormal bleeding between period
- heavy bleeding after period
- heavy bleeding after period ends
- heavy bleeding between periods
- heavy bleeding during ovulation
- heavy bleeding during period
- heavy bleeding in between periods
- heavy bleeding perimenopause
- heavy bleeding with clots
- heavy blood clots during period
- heavy clotting during period
- heavy flow period
- heavy irregular bleeding between periods
- heavy irregular periods
- heavy menstrual bleeding
- heavy menstrual bleeding causes
- heavy menstrual bleeding with clots
- heavy menstrual discharge
- heavy monthly bleeding
- heavy period after pregnancy
- heavy period blood clots
- heavy period causes
- heavy period clots
- heavy period with clots
- heavy periods
- heavy periods and spotting in between
- heavy periods treatment
- heavy periods with blood clots
- heavy prolonged menstrual bleeding
- heavy spotting
- heavy spotting after period
- heavy spotting between periods
- how to calculate period cycle
- how to count period cycle
- how to get your period
- how to stop heavy periods
- how to stop menstrual bleeding
- how to stop period
- how to stop period bleeding
- how to stop period pain
- how to stop your period early
- i have bleeding between periods
- in between period bleeding
- information on women
- intermenstrual bleeding
- intermittent bleeding between periods
- irregular bleeding
- irregular bleeding after period
- irregular bleeding between periods
- irregular bleeding during period
- irregular heavy bleeding between periods
- irregular heavy periods
- irregular menstruation causes
- irregular period spotting
- irregular periods
- irregular periods and spotting
- irregular periods and spotting in between
- irregular periods causes
- irregular periods symptoms
- irregular spotting
- irregular spotting after period
- irregular spotting between periods
- irregular spotting causes
- keep bleeding after period
- keep spotting after period
- ladies health
- ladies health and fitness
- ladies health care
- ladies health problems
- large blood clots during period
- late period
- light bleeding after menstrual cycle
- light bleeding after menstruation
- light bleeding after period
- light bleeding after period ends
- light bleeding after period finished
- light bleeding after period was over
- light bleeding between periods
- light bleeding in between periods
- light blood after period
- light blood spotting after period
- light menstrual bleeding
- light period
- light spotting after period
- light spotting between periods
- light spotting in between periods
- long heavy period
- long menstrual bleeding
- long menstrual period
- long menstrual period causes
- long menstrual periods
- long period bleeding
- long periods
- long periods menstrual bleeding
- long spotting after period
- men health
- menopause symptoms
- mens health
- menstrual bleeding after period
- menstrual bleeding between periods
- menstrual bleeding for 3 weeks
- menstrual bleeding for a month
- menstrual bleeding in between periods
- menstrual cycle
- menstrual cycle bleeding
- menstrual cycle bleeding between periods
- menstrual cycle phases
- menstrual cycle spotting
- menstrual cycle spotting after period
- menstrual cycle symptoms
- menstrual period
- menstrual period symptoms
- menstrual spotting
- menstrual spotting after period
- menstrual spotting causes
- menstruation
- mild bleeding between periods
- missed period
- monthly period cycle
- more bleeding after period
- my period
- my period is late
- national women's health information center
- no bleeding in periods
- non menstrual bleeding
- normal period cycle
- not bleeding during period
- not bleeding on my period
- occasional bleeding between periods
- older women's health issues
- on and off bleeding after period
- over bleeding after period
- ovulation period
- painful periods
- passing blood clots during period
- period
- period after spotting
- period blood
- period blood clots
- period calculator
- period calendar
- period cramps
- period cramps but no period
- period cycle
- period cycle calculator
- period pain
- period pain but no period
- period problems
- period spotting
- period spotting after period
- period spotting causes
- period symptoms
- period tracker
- periods bleeding
- periods in women
- persistent bleeding between periods
- pms symptoms
- post menstrual cycle bleeding
- post period bleeding
- post period spotting
- pre period symptoms
- prolonged light bleeding after period
- prolonged menstrual bleeding with clots
- prolonged menstrual period
- prolonged period
- pv bleeding
- really heavy period
- really heavy period with clots
- reason of spotting after periods
- reasons for a missed period
- reasons for bleeding after period
- reasons for bleeding between periods
- reasons for irregular periods
- reasons for late period
- reasons for spotting after period
- red blood after period
- red spotting after period
- regular bleeding between periods
- remedy for heavy menstrual bleeding
- s health
- short heavy period
- signs of menstrual cycle
- signs of period
- signs of your period
- slight bleeding after period
- slight bleeding between periods
- slight bleeding in between periods
- small bleeding after period
- small bleeding between periods
- spot bleeding
- spot bleeding after period
- spot bleeding between periods
- spot bleeding in between periods
- spotting a week after period
- spotting after a period
- spotting after a period ends
- spotting after cycle
- spotting after menses
- spotting after menstrual cycle
- spotting after menstrual cycle ends
- spotting after menstrual period
- spotting after menstruation
- spotting after my period
- spotting after period
- spotting after period ends
- spotting after period normal
- spotting after periods causes
- spotting and bleeding
- spotting and discharge after period
- spotting between cycles
- spotting between menstrual cycles
- spotting between periods
- spotting between periods after pregnancy
- spotting between periods causes
- spotting between periods normal
- spotting bleeding after period
- spotting blood
- spotting blood after period
- spotting blood between periods
- spotting during cycle
- spotting during menstruation
- spotting during period
- spotting everyday after period
- spotting for a week after period
- spotting in between cycles
- spotting in between periods
- spotting in between periods causes
- spotting in menstrual cycle
- spotting in menstruation
- spotting in periods
- spotting just after period
- spotting menstrual
- spotting menstrual cycle
- spotting menstrual period
- spotting not period
- spotting period
- spotting periods causes
- spotting week after period
- spotty bleeding between periods
- start bleeding after period
- still bleeding after menstrual cycle
- still bleeding after period
- still slightly bleeding after period
- still spotting after period
- still spotting after period ends
- stomach pain during periods
- stop menstrual bleeding
- stop period bleeding
- super heavy period
- symptoms before period
- symptoms of a period
- symptoms of getting your period
- symptoms of menstrual cycle
- symptoms of period
- symptoms of period coming
- symptoms of spotting after period
- the healthy woman
- topics on women's issues
- treatment for heavy periods
- treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding
- Uncategorized
- unusual bleeding between periods
- unusual menstrual bleeding
- unusual spotting
- unusual spotting between periods
- unusually heavy period
- uterine bleeding between periods
- very heavy period
- very heavy periods
- very light bleeding after period
- very light period
- ways to stop your period
- what can cause abnormal bleeding
- what can cause bleeding between periods
- what can cause bleeding in between periods
- what can cause heavy bleeding between periods
- what can cause irregular bleeding
- what can cause light bleeding between periods
- what can cause spotting between periods
- what can cause spotting in between periods
- what can cause you to bleed after your period
- what causes a heavy period
- what causes a woman to bleed in between periods
- what causes abnormal bleeding between periods
- what causes bleeding after menstruation
- what causes bleeding after period
- what causes bleeding after period ends
- what causes bleeding before your period
- what causes bleeding between periods
- what causes bleeding in between periods
- what causes constant bleeding between periods
- what causes continuous bleeding after period
- what causes heavy bleeding between periods
- what causes heavy menstrual bleeding
- what causes heavy periods
- what causes irregular bleeding between periods
- what causes irregular periods
- what causes irregular periods and spotting
- what causes light bleeding after period
- what causes light bleeding between periods
- what causes light bleeding during periods
- what causes light spotting between periods
- what causes period cramps
- what causes period pains
- what causes period spotting
- what causes spotting
- what causes spotting a week after period
- what causes spotting after a period
- what causes spotting after period
- what causes spotting after period ends
- what causes spotting after your period
- what causes spotting between periods
- what causes spotting during period
- what causes spotting in between periods
- what could cause bleeding after my period
- what could cause bleeding between periods
- what could cause spotting between periods
- what helps period pains
- what is a period
- what would cause a woman to bleed between periods
- what would cause bleeding between periods
- what would cause spotting
- when is my next period
- when is my period due
- why am i spotting
- why are my periods irregular
- why do women have periods
- why is my period early
- why is my period late
- woman bleeding after period
- woman health
- woman s health
- woman spotting between periods
- woman's health insurance
- woman's health services
- womans health
- womans health magazine
- womans magazine
- women
- women & health
- women and health
- women and health issues
- women and healthcare
- women bleeding between periods
- women for health
- women health issues over 50
- women health tips
- women healthy
- women in health
- women information
- women over 50 health issues
- women period
- women period cycle
- women related topics
- women s
- women shealth
- women sites
- women topics
- women website
- women's fitness website
- women's fitness websites
- women's health
- women's health Abilene
- women's health Akron
- women's health Albuquerque
- women's health Alexandria
- women's health Allentown
- women's health Amarillo
- women's health Anaheim
- women's health Anchorage
- women's health and fitness
- women's health and wellness
- women's health Ann Arbor
- women's health Antioch
- women's health Arlington
- women's health articles
- women's health Arvada
- women's health Athens
- women's health Atlanta
- women's health Augusta
- women's health Aurora
- women's health awareness
- women's health Bakersfield
- women's health Baltimore
- women's health Baton Rouge
- women's health Beaumont
- women's health Bellevue
- women's health Berkeley
- women's health Billings
- women's health Birmingham
- women's health Boise
- women's health Boulder
- women's health Bridgeport
- women's health Broken Arrow
- women's health Browning
- women's health Brownsville
- women's health Burbank
- women's health Cambridge
- women's health Cape Coral
- women's health care
- women's health care clinic
- women's health Carlsbad
- women's health Carrollton
- women's health Cary
- women's health Cedar Rapids
- women's health Centennial
- women's health center
- women's health Chandler
- women's health Charleston
- women's health Chattanooga
- women's health Chesapeake
- women's health Chula Vista
- women's health Cincinnati
- women's health Clarksville
- women's health Clearwater
- women's health Cleveland
- women's health clinic
- women's health Colorado Springs
- women's health Columbia
- women's health Columbus
- women's health com
- women's health Concord
- women's health Coral Springs
- women's health Corona
- women's health Corpus Christi
- women's health Costa Mesa
- women's health Cut Bank
- women's health Daly City
- women's health Davenport
- women's health day
- women's health Dayton
- women's health Denton
- women's health Des Moines
- women's health diet
- women's health doctors
- women's health Downey
- women's health Durham
- women's health El Cajon
- women's health El Monte
- women's health Elgin
- women's health Elizabeth
- women's health Elk Grove
- women's health Erie
- women's health Escondido
- women's health Eugene
- women's health Evansville
- women's health Everett
- women's health Fairfield
- women's health Fargo
- women's health Fayetteville
- women's health fitness
- women's health Flint
- women's health Fontana
- women's health Fort Lauderdale
- women's health Fort Wayne
- women's health Fremont
- women's health Fresno
- women's health Frisco
- women's health Fullerton
- women's health Gainesville
- women's health Garden Grove
- women's health Garland
- women's health Gilbert
- women's health Glendale
- women's health Grand Rapids
- women's health Great Falls
- women's health Green Bay
- women's health Greensboro
- women's health Gresham
- women's health Hampton
- women's health Hartford
- women's health Hayward
- women's health Henderson
- women's health Hialeah
- women's health High Point
- women's health Hollywood
- women's health Honolulu
- women's health Huntington Beach
- women's health Huntsville
- women's health Independence
- women's health information
- women's health Inglewood
- women's health insurance
- women's health Irvine
- women's health Irving
- women's health issues list
- women's health issues topics
- women's health Jackson
- women's health Jersey City
- women's health Joliet
- women's health Kalispell
- women's health Kansas City
- women's health Kenosha
- women's health Kent
- women's health Killeen
- women's health Knoxville
- women's health Lafayette
- women's health Lakewood
- women's health Lancaster
- women's health Lansing
- women's health Laredo
- women's health Las Cruces
- women's health Las Vagas
- women's health Lexington
- women's health Lincoln
- women's health Little Rock
- women's health Long Beach
- women's health Louisville
- women's health Lowell
- women's health Lubbock
- women's health Madison
- women's health mag
- women's health magazine
- women's health McAllen
- women's health McKinney
- women's health Mesa
- women's health Mesquite
- women's health Miami
- women's health Miami Gardens
- women's health Midland
- women's health Milwaukee
- women's health Minneapolis
- women's health Miramar
- women's health Mobile
- women's health Modesto
- women's health Montgomery
- women's health Moreno Valley
- women's health Murrieta
- women's health Naperville
- women's health Nashville
- women's health network
- women's health New Haven
- women's health Newark
- women's health Newport News
- women's health Norfolk
- women's health Norman
- women's health North Charleston
- women's health North Las Vegas
- women's health Norwalk
- women's health Oakland
- women's health Oceanside
- women's health Odessa
- women's health Oklahoma
- women's health Olathe
- women's health Omaha
- women's health online
- women's health Ontario
- women's health Orange
- women's health organizations
- women's health Orlando
- women's health Overland Park
- women's health Oxnard
- women's health Palm Bay
- women's health Palmdale
- women's health Pasadena
- women's health Paterson
- women's health Pembroke Pines
- women's health Peoria
- women's health Pittsburgh
- women's health Plano
- women's health Pomona
- women's health Pompano Beach
- women's health Port St. Lucie
- women's health Portland
- women's health problems
- women's health program
- women's health programs
- women's health Providence
- women's health Provo
- women's health Pueblo
- women's health questions
- women's health Raleigh
- women's health Reno
- women's health Rialto
- women's health Richardson
- women's health Richmond
- women's health Riverside
- women's health Rochester
- women's health Rockford
- women's health Roseville
- women's health Round Rock
- women's health Sacramento
- women's health Saint Paul
- women's health Salem
- women's health Salinas
- women's health Salt Lake City
- women's health San Bernardino
- women's health San Buenaventura
- women's health Santa Ana
- women's health Santa Clara
- women's health Santa Clarita
- women's health Santa Maria
- women's health Santa Rosa
- women's health Savannah
- women's health Scottsdale
- women's health services
- women's health Shreveport
- women's health Simi Valley
- women's health Sioux Falls
- women's health site
- women's health South Bend
- women's health Spokane
- women's health Springfield
- women's health St. Louis
- women's health St. Petersburg
- women's health Stamford
- women's health Sterling Heights
- women's health Stockton
- women's health subscription
- women's health Sunnyvale
- women's health Surprise
- women's health Syracuse
- women's health Tacoma
- women's health Tallahassee
- women's health Tampa
- women's health Temecula
- women's health Tempe
- women's health Thornton
- women's health Thousand Oaks
- women's health Toledo
- women's health Topeka
- women's health topics
- women's health Tucson
- women's health Tulsa
- women's health Vallejo
- women's health Vancouver
- women's health Victorville
- women's health Virginia Beach
- women's health Visalia
- women's health Waco
- women's health Warren
- women's health Washington
- women's health Waterbury
- women's health websites
- women's health West Covina
- women's health West Jordan
- women's health West Palm Beach
- women's health West Valley City
- women's health Westminster
- women's health Wilmington
- women's health Winston–Salem
- women's health Worcester
- women's health Yonkers
- women's healthcare center
- women's magazines
- women's medical issues
- women's mental health
- women's websites
- womens health advice
- womens health and fitness magazines
- womens health issues
- womens health magazine subscription
- womens health service
- womens health uk
- womens healthy diet
- womens helth
- womenshealth gov
- womenshealthmag
- womenshealthmag com
- www women
- www women body
- www womenshealth
- www womenshealth gov
- www womenshealthmag com
- young women health
 admin
admin